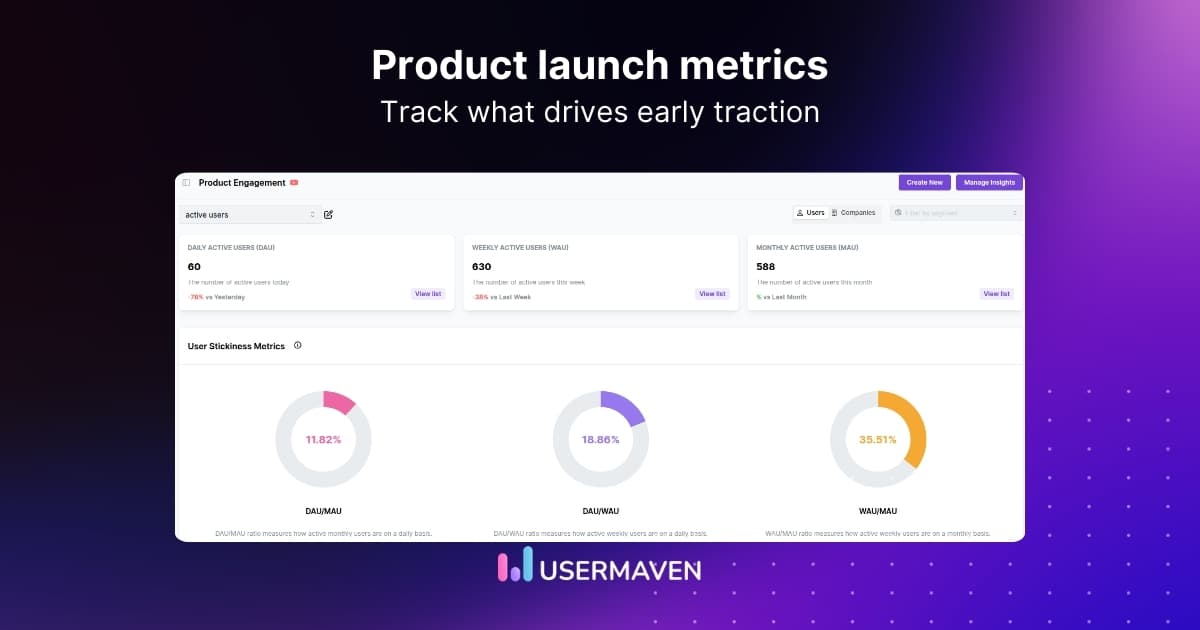
The value of scroll depth and how to track it
Jan 20, 2026
7 mins read
Written by Imrana Essa

Most website visitors don’t read a page from top to bottom.
They skim, pause, scroll, and leave often without clicking anything. What matters isn’t just who lands on your page, but how far they actually engage with it along their customer journey.
This is where understanding the value of scroll depth becomes critical. Scroll depth reveals which sections of a page truly capture attention and where users lose interest. Instead of relying on assumptions, it shows how real visitors interact with your content.
By monitoring scroll depth, teams can uncover scrolling patterns, improve content structure, and make smarter UX and conversion decisions. In this article, we’ll explore what scroll depth is, why it matters, and how to track it effectively.
What is scroll depth
Scroll depth is a behavioral engagement metric that measures how far a user scrolls down a webpage during a session.
It’s typically expressed as a percentage, indicating how much of the page’s content a visitor has viewed.
For example, if a user scrolls halfway down a page, their scroll depth is recorded as 50%. If they reach near the footer, it may register as 90–100%, depending on how tracking is configured.
Scroll depth is commonly analyzed alongside other engagement metrics such as:
- Time on page
- Bounce rate
- Click-through rate
- Conversion events
Together, these metrics help website owners, marketers, UX designers, and product teams understand user behavior with content, layouts, and page structure.
Unlike simple pageview metrics, scroll depth provides context. It helps answer questions like:
- Are users actually consuming the content?
- Which sections are being skipped?
- Where does attention drop off?
Scroll depth matters more than pageviews: Here’s why
A pageview only confirms that a page loaded. It doesn’t tell you whether users read, scrolled, or engaged meaningfully.
Scroll depth fills that gap by showing:
- How far users progress through a page
- Whether key messages are seen
- If important CTAs are positioned effectively
For content-heavy pages, scroll depth helps determine whether users are truly engaging or abandoning early. For conversion-focused pages, it highlights whether users even reach critical sections like pricing, testimonials, or forms.
In short, scroll depth connects traffic to behavior, making it far more actionable than vanity metrics alone.
Unlock insights that drive growth
*No credit card required
What is a good scroll depth
There’s no single “good” scroll depth that applies to every website. What qualifies as strong engagement depends on the page type, content length, user intent, and page goal.
That said, practical benchmarks can help you interpret performance more realistically.
Scroll depth benchmarks by page type
Scroll depth benchmarks help set expectations, but they should never be treated as universal targets. What matters most is whether users reach the sections that support your page’s goal.
- Landing pages:
20–40% can still be effective if CTAs and value propositions appear early. - Blog posts and long-form content:
60–80% usually indicates strong engagement and content relevance. - Product pages:
40–70% suggests users are exploring features, benefits, and social proof. - Documentation and guides:
75%+ often reflects successful content flow and clarity.
Instead of chasing an arbitrary percentage, focus on where users stop scrolling and whether that aligns with your page’s purpose.
Key considerations when evaluating scroll depth
Most scroll tracking tools rely on predefined thresholds like 25%, 50%, 75%, and 100%. While convenient, this approach can introduce inaccuracies.
For example:
- A user scrolling to 38% is recorded as 25%
- A critical section at 42% may appear “unseen”
- Engagement patterns get blurred between intervals
This makes it important to interpret scroll depth carefully and, where possible, use more granular tracking.
When defining what “good” scroll depth means for your site, consider:
- Content structure:
Long-form pages naturally require deeper scrolling than short landing pages. - User intent:
Informational content benefits from depth, while action-driven pages may not. - Page goals:
High scroll depth is less important if users convert early.
Scroll depth should always be evaluated in context, not in isolation.
Scroll depth vs scroll rate vs average page depth
These metrics are often confused, but they measure different aspects of user behavior.
| Metric | What it measures | Best used for |
| Scroll depth | How far users scroll on a page | Content engagement and layout effectiveness |
| Scroll rate | Speed or frequency of scrolling | Reading behavior and UX testing |
| Average page depth | Pages viewed per session | Navigation and journey analysis |
Scroll depth focuses on vertical engagement, while average page depth reflects horizontal navigation. Combining both provides a clearer picture of how users move through your site and content.
See what's working. Fix what's not. Grow faster.
*No credit card required
Scroll depth vs engagement
Scroll depth is often used as a proxy for engagement, but the two are not the same. While scroll depth measures how far users scroll, engagement reflects how meaningfully they interact with a page.
A user can scroll deeply without being engaged, for example, by quickly skimming or jumping through content. Conversely, a user may engage heavily with a specific section, click CTAs, or interact with elements without scrolling far.
This is why scroll depth works best when analyzed alongside engagement metrics such as:
- Time on page
- Clicks and interactions
- Conversion events
When deeper scroll depth consistently aligns with longer sessions or higher interaction rates, it becomes a strong signal of genuine engagement. On its own, however, scroll depth should be treated as a directional indicator rather than a standalone engagement metric.
Scroll depth vs conversion impact
High scroll depth does not automatically mean higher conversions, but it plays an important role in understanding conversion behavior.
For conversion-focused pages, scroll depth helps answer key questions such as:
- Do users reach pricing, testimonials, or forms before converting?
- Are users scrolling deeply but failing to take action?
- Do high-converting users follow different scroll patterns?
In many cases, shallow scroll depth combined with high conversions indicates strong messaging and effective CTA placement. On the other hand, deep scrolling without conversions may signal unclear value propositions, friction, or decision fatigue.
The significance of scroll depth
Scroll depth offers insights that directly impact UX, content strategy, and conversion optimization.
1. Data-driven decision-making
Over time, monitoring scroll depth can help you identify trends and patterns in user behavior. For example, you might notice changes in scroll depth based on seasonality, marketing campaigns, or content updates.
Scroll depth data lets you make data-driven decisions about your website’s design, content strategy, and user experience. It can help you prioritize improvements and allocate resources effectively.
2. User engagement and experience
Scroll depth is a strong indicator of engagement quality. Deep scrolling often signals interest, relevance, and trust, while shallow scrolling may point to:
- Weak introductions
- Poor layout
- Mismatched intent
It’s also valuable for mobile analysis, where scrolling behavior differs significantly due to screen size and interaction patterns.
3. Content performance and optimization
Scroll depth helps you evaluate the performance of different sections of your webpage or individual pieces of content. You can identify which parts of your content capture user attention and which need improvement.
By analyzing scroll depth data, you can pinpoint areas of your webpage where users tend to drop off or lose interest. It can guide you in optimizing those sections to keep users engaged on your site longer.
Scroll depth also contributes to crafting a polished content strategy. If users scroll past a certain point consistently, it may indicate a need for more content in that area or a different content structure to serve user needs better.
4. Conversion tracking
For websites with specific conversion goals, such as e-commerce sites or lead generation pages, scroll depth can be a valuable component of conversion tracking. It lets you understand how far users scroll before taking a desired action, which can inform conversion rate optimization efforts.
When conducting A/B tests to optimize various elements of your webpage, including layout, content, or calls to action, scroll depth can be a valuable metric to determine which version performs better regarding user engagement and retention.
How to track scroll depth effectively
There are multiple ways to track scroll depth, each with different levels of accuracy, flexibility, and effort.
1. Third-party website analytics tools
Many modern analytics tools offer built-in scroll tracking with visual reporting and behavior insights.
Popular options include Usermaven, Hotjar, and Crazy Egg.
Advantages:
- Easy setup
- Visual dashboards
- Session replays and heatmaps
- Minimal technical effort
Limitations:
- Fixed scroll thresholds
- Limited customization
- Potential privacy concerns
- Data sampling or delays
The effectiveness of these tools depends on how granular and flexible their scroll tracking capabilities are.
2. JavaScript
The JavaScript programming language can be used to measure scroll depth by adding custom scripts to your web pages.
It offers full control over scroll tracking implementation, allowing you to customise it to your requirements. You can set custom scroll depth thresholds and trigger events or actions based on user scroll behavior.
Implementing scroll tracking using JavaScript doesn’t rely on third-party tools or services, giving you full autonomy over your tracking. You can access scroll depth data in real time, which can be valuable for immediate analysis and feedback.
However, implementing scroll tracking with JavaScript requires coding skills, making it less accessible for non-developers. Custom JavaScript implementation can be time-consuming, especially for complex tracking scenarios. Also, you are responsible for maintaining and updating the tracking code, which can become cumbersome as your website evolves.
3. Google Analytics and Google Tag Manager
Google Analytics (GA) and Google Tag Manager (GTM) provide a more user-friendly way to track scroll depth without extensive coding.
Easy integration with Google Analytics allows for easy consolidation of scroll depth data with other website analytics. GTM offers predefined triggers for common scroll depth thresholds (e.g., 25%, 50%, 75%, 100%), simplifying implementation. Once set up, GTM and GA tracking require minimal maintenance, and updates are managed within the platforms.
While GTM and GA provide easy implementation, they may lack the level of customization and flexibility that advanced users or complex tracking scenarios require. Data collected through GTM and GA may not be available in real time, and a GA4 data delay can occur before insights are ready for analysis. Since this setup relies on Google’s tracking services, it may also not align with certain data privacy or compliance requirements.
Drive business growth
with AI-powered analytics
*No credit card required
Tracking scroll depth with Usermaven
Usermaven enables more accurate scroll depth tracking by moving beyond rigid percentage-based thresholds. Instead of relying only on fixed points like 25%, 50%, 75%, or 100%, it helps teams understand how users actually scroll through landing pages and long-form content.
Once tracking is set up, scroll depth data is captured automatically alongside other engagement metrics, without the need for custom scripts or complex configurations.
The video below explains how scroll depth and engagement metrics are tracked in Usermaven.
Track scroll depth beyond fixed thresholds
Standard scroll tracking often misses important interactions when key sections don’t align with predefined percentages. Usermaven allows teams to analyze scroll behavior in a more flexible way that reflects real content structure.
This is especially useful when:
- CTAs appear mid-page
- Content length varies significantly
- Important sections fall between standard scroll points
Analyze scroll behavior in context with other metrics
Scroll depth becomes more actionable when viewed alongside other engagement signals. As the best marketing attribution software for SaaS teams, Usermaven connects scroll data with metrics including session duration, engagement events, and conversions.
This makes it easier to identify whether deeper scrolling correlates with higher engagement or conversion activity.

Improve content structure and CTA placement
By highlighting consistent drop-off points, Usermaven helps teams refine content layout and hierarchy. If users frequently stop scrolling before a key section, it signals the need to reassess placement, messaging, or visual flow.
These insights are particularly valuable for landing pages, long-form content, and product pages with detailed explanations.
Support long-form content and complex user journeys
For pages with extensive content or multi-step customer journeys, Usermaven helps teams compare scroll engagement across different page types and identify sections that consistently lose attention.
This supports better decisions around content depth, sequencing, and user flow across the customer journey.
Privacy-friendly scroll tracking
Usermaven’s scroll depth tracking is cookie-less and compliant with regulations such as GDPR and CCPA, allowing teams to collect reliable engagement data while maintaining strong privacy standards.
The easiest GA4 alternative for marketers and product teams
*No credit card required
To sum it up
Scroll depth helps you understand how users actually engage with a page, where attention drops, and which sections influence decisions across the customer journey. When analyzed in context, it becomes a practical signal for improving content structure, user experience, and conversion performance.
Usermaven helps solve this by enabling precise scroll depth tracking and deeper behavioral analysis using cookie-less, white-label pixel tracking, ensuring accurate data even when ad blockers are present. As a modern website analytics tool, it connects scroll behavior with attribution, funnels, and engagement insights while maintaining full data ownership and privacy compliance.
Want a clearer view of how users scroll, engage, and convert across your site? Start a free trial or book a demo today with Usermaven.
FAQs
What is the average scroll depth?
The average scroll depth on a website varies depending on factors like content type and user behavior. Generally, a scroll depth of 75% is considered good for a webpage with long-form content. A depth of 50% or less might be good for conversion-focused websites.
Why is natural scrolling better?
Many users and experts argue that natural scrolling is better for several reasons. Natural scrolling aligns the digital experience more closely with real-world physical actions. It reduces cognitive load because users don’t need to think about a separate set of rules for scrolling on digital devices compared to physical actions.
What are the different types of scrolling?
There are several different types of scrolling methods, each designed to provide a unique user experience. Long, infinite, and parallax scrolling are some scrolling types.
What is the difference between parallax and infinite scrolling?
Parallax scrolling creates an illusion of depth by moving different layers of content at different speeds as the user scrolls, while infinite scrolling continuously loads new content as the user reaches the bottom of a page or list, commonly used in social media feeds.
Why is 90% scroll depth considered as reaching the bottom of a page?
Larger websites usually have the footer as an extra navigation menu, offering convenient quick links for users to explore further. It is especially beneficial on smartphones, where reaching the top to access navigation menus can be cumbersome.
Why is scroll depth important for SEO?
Scroll depth is important for SEO because it helps measure how users engage with content beyond pageviews. While it’s not a direct ranking factor, deeper scroll depth often indicates relevant, high-quality content and better user experience, which can indirectly support stronger search performance over time.
How to track scroll depth and user interaction on landing pages?
On landing pages, scroll depth should be analyzed alongside:
– CTA clicks
– Form interactions
– Conversion events
If users convert early, shallow scroll depth isn’t a problem. But if users scroll deeply without converting, it may indicate unclear messaging or weak CTAs.
How to track scroll and navigation patterns together?
Scroll depth shows how far users go. Navigation analysis shows where they go next.
Combining both reveals:
– Content influence on navigation
– Drop-off points before exits
– How users move through key pages
This combined view offers a more complete understanding of user behavior and intent.
Try for free
Grow your business faster with:
- AI-powered analytics & attribution
- No-code event tracking
- Privacy-friendly setup