Table of contents
The complete guide to product metrics for product managers
Dec 7, 2022
6 mins read
Written by Usermaven
A fully optimized product manager can increase company profits by over 34%. Product managers use product metrics to drive product growth and implement a product roadmap. As a result, these metrics are the most prominent tool for product managers in decision-making.
Product metrics are widely used for better results and performance tracking. They resolve challenges faced by the product teams. Product managers face challenges in choosing the best data analytics tool, the right metrics and bridging the gap between the two to extract valuable insights.
This article is a comprehensive guide to the top product metrics in product management. It outlines why they matter and how you can nurture your product with the right metrics.
What are product metrics & why do they matter?
Product metrics are quantitative performance measures that a brand tracks and analyzes to forecast the success of its product. Product metrics examples include conversion rate, churn rate, and customer retention rate.
Product metrics are quantitative performance measures that a brand tracks and analyzes to forecast the success of its product. Product metrics examples include conversion rate, churn rate, and customer retention rate.
Great products are data-backed. Product, sales, and marketing teams use data-driven insights to gauge customer behavior and nurture customer relations. Product metrics link to the product strategy and indicate how users interact with your product.
Here’s why product metrics are essential.
- Enable informed decision making – Data metrics assist a company in continually enhancing its product. Such metrics, also known as key performance indicators (KPIs), act as quantitative evidence for a company that tells about which aspects of the product resonate with its customers.
- Get approvals from executives – Obtaining executive approvals becomes straightforward with product metrics. Product metrics offer data-backed objectives for strategies and product roadmaps. With metrics as evidence, executives can foresee the impact of their decisions on the business’s growth.
- Better team alignment – With product metrics, teams are better aligned. They provide all teams (whether design, development, or marketing) with a common goal.
- Comparative analysis – Tracking product metrics reveals whether your business is over- or underperforming in the industry benchmarks.
- Problems identification – Analyzing the product metrics helps identify emerging problems and correct them before they become pain points.
You might also find this interesting: Essential Product Marketing KPIs
Power up your SaaS
with perfect product analytics
*No credit card required
Product metrics vs business metrics – when to use what
Business metrics are quantifiable measures businesses use to track, monitor, and assess the failure and success of business processes. They are essential to communicate an organization’s progress in achieving short and long-term objectives. Business metrics fall under categories such as finance, marketing, human resources, information technology, investment, and more.
Business metrics are quantifiable measures businesses use to track, monitor, and assess the failure and success of business processes. They are essential to communicate an organization’s progress in achieving short and long-term objectives. Business metrics fall under categories such as finance, marketing, human resources, information technology, investment, and more.
Business metrics are of lagging nature. These are your business performance results after some time, such as at the end of the financial year. VCs and investors extensively use business metrics.
Below are some of the widely used business metrics related to different categories:
Financial metrics
- Working Capital
- Gross Profit Margin
- Net Cash Flow
- Debt-to-Equity Ratio
Marketing metrics
- Conversion Rate
- Cost of Customer Acquisition
Sales metrics
- Sales Cycle
- Average Customer Revenue
- Total Customers
- Customer Retention Rate
In contrast, product metrics focus on evaluating the success of a business’s products. They are different from business metrics in terms of their leading nature. Product metrics are early indicators of success. You can broadly categorize them as traffic, monetization, and engagement metrics. Product managers use product metrics to correct their efforts if the product is underperforming.
Both metrics are vital to measuring business and product performance. Together they paint the whole canvas of your business growth.
How to pick the right product metrics to track and optimize
Choosing the right product metrics is directly linked to the success of your product. The KPIs you select will depend on your business model. Keep in mind the following essential pointers while picking the right product metrics.
- Not all products are the same – It’s usual for a business to have different product metrics for its various products. No two products might be treated the same based on their functionalities and target audience.
- The right product metrics start with the right questions – “What isn’t measured can’t be improved.” Choosing the right metric starts with asking the right questions. Figure out what you want to measure and why.
- Finding the right questions takes collaboration – Collaboration and teamwork open the doors to asking the right questions. This process indulges all teams of the company and can benefit from everyone’s curiosity and expertise.
- Look for metrics that best suits your product – Not all metrics represent your product and users. So, focus on the metrics that are most relevant to your product.
- Never ignore where is your product in the life cycle – The stage of your product in its life cycle determines the product metrics you must implement. If you have already launched a product, you can focus on metrics that show user engagement and behavior. But if you want to build a business case for investment, look at metrics that predict the revenue over time, such as ARPU.
- Keep in mind the stakeholders for your product metrics – Although your company might define product success metrics, product managers must also have specific product metrics to guide their efforts. Product management, sales, and leadership teams can benefit significantly from product metrics. Thinking about who will benefit from each helps to communicate more effectively.
For instance, video streaming services or social media apps focus on the daily active users (DAU). In contrast, the e-commerce website might not benefit from the daily customer visits. A valuable metric for it is the number of orders placed.
Top metrics that matter in product management
Let’s dive deep into the top metrics for product management.
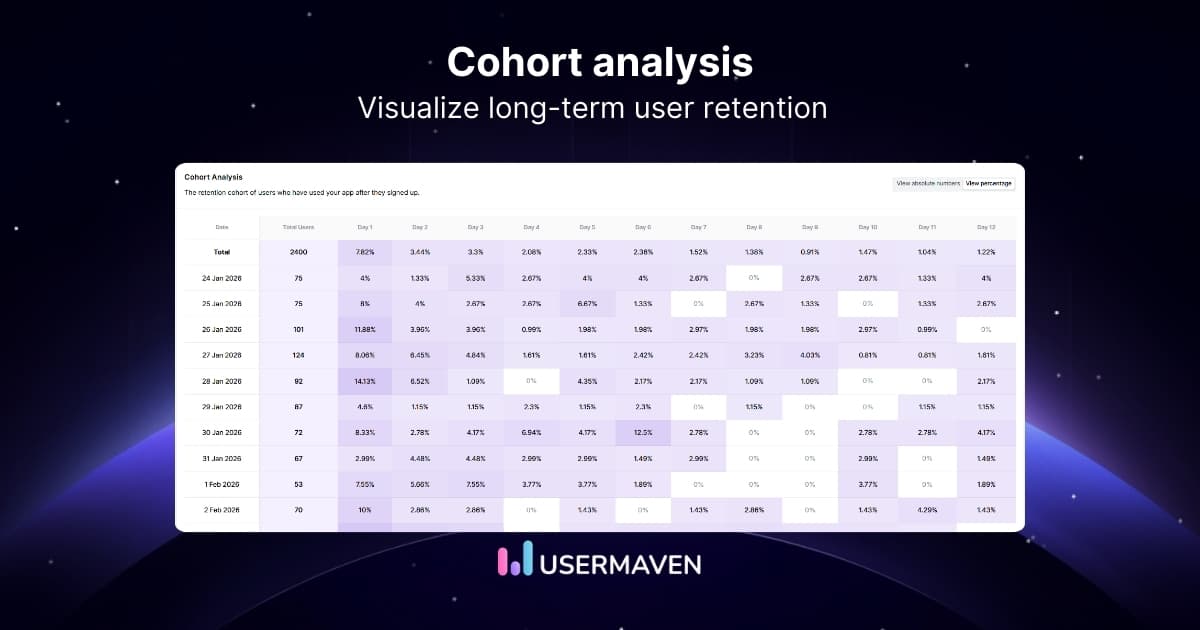
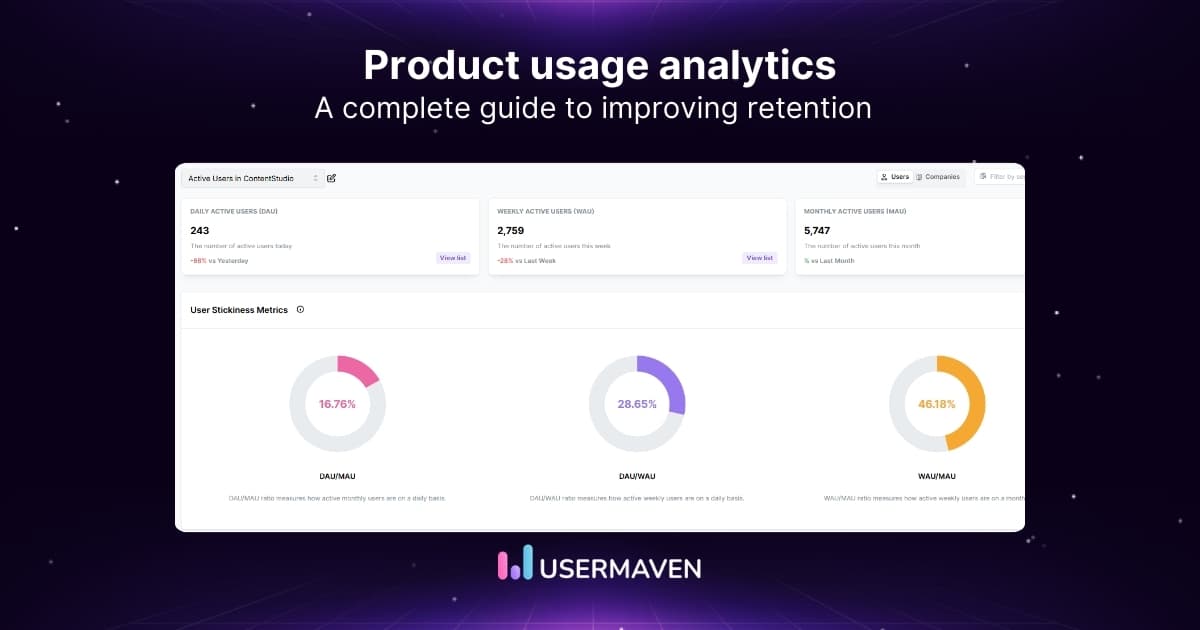
Monthly active users (MAU) & daily active users (DAU)
Active user metrics are a way to measure the stickiness of your product. If your customers keep returning to use the product, it reflects high user engagement. It means your product is delivering value to your existing customers. It also helps in customer retention.
Active users are primarily measured on a daily or monthly basis. They represent the total number of unique users in a day or during a month. Average daily or monthly active users are other critical numbers.
An even better way to measure stickiness is the DAU/MAU ratio. DAU to MAU is the ratio of the monthly proportion of active users who engage with your product in a single day. This ratio helps to understand how valuable your product is to customers. In addition, this ratio gives you the essential context for understanding the level of engagement and potential revenue.
The formula for the DAU/MAU ratio is straightforward:
Customer conversion rate
Customer conversion rate measures how many customers take the desired action when they land on your product page. A high conversion rate means people like your offering and can get it. If your conversion rate is minimum, it means that there are barriers preventing customers from buying your product.
To calculate the product’s conversion rate, divide the total conversions by the number of unique visitors.
Customer churn rate
Churned users mean customers who have signed off or are no longer active. Customer churn rate is the percentage of customers that leave or sign off in a given time. For instance, your annual churn rate is the percentage of customers going per year. There are four types of churn: proactive churn, reactive churn, happy churn, and fake churn.
The churn rate can be calculated as follows;
Customer retention rate
The customer retention rate is the percentage of users that sign up or keep utilizing your services. The customer retention rate is also called the renewal rate. The retention rate can be calculated on a month-to-month or annual basis.
The formula for the retention rate is given as follows;
- Where E is the total number of users at the end of the time period
- N is the total number of new users
- S is the total number of existing users at the beginning
Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT Score) & Net Promoter Score (NPS)
Both are customer experience metrics that measure the extent to which your customers enjoy your product or service. CSAT measures short-term user satisfaction with a service or product. And NPS is a long-term indication of user loyalty and satisfaction.
Use the following formula to measure the percentage CSAT score:
NPS is based on user feedback responses on a scale of 1-10 to a survey question. “How likely are you to recommend [your product] to a colleague or friend?” is the NPS question. You can categorize the customer responses based on the below ranges.
- 9-10 are promoters – they are satisfied with the product and happy to tell others about it.
- 7-8 are passive – they are not fully satisfied with the product and can demotivate potential customers.
- 0-6 are detractors – they are dissatisfied with the product and might switch to a competitor.
Measuring the NPS score is simple, add up your responses and subtract the percentage of detractors from promoters.
The formula for calculating the NPS score is as follows;
For instance, if 60% of the respondents are promoters, 30% are detractors, and 10% are passives, the NPS score would be 30.
Customer lifetime value (LTV)
The customer lifetime value (CLV) measures how much a business can earn from a typical customer as long as that person remains a client. When calculating the CLV, it’s vital to look at the average revenue made by a customer and the total profit.
It provides essential insights into,
- How do the customers interact with your business?
- Is your marketing strategy working as expected?
Understanding what you earn from an average customer can increase or decrease your spending to ensure maximum profitability and attract the right customers.
Customer acquisition cost (CAC)
The customer acquisition cost (CAC) is an essential product metric that measures how much a business spends to acquire new customers. It helps a company evaluate the overall value of a customer to the company.
The super simple way to CAC is by dividing the total costs to acquire customers by the total no of customers acquired at a given time.
- MCC is the total marketing campaign expenses related to the acquisition
- CA is total acquired customers
Monthly recurring revenue (MRR) & annual recurring revenue
MRR and ARR are essential factors that every SaaS business needs to understand and monitor. Monthly recurring revenue is the sum of subscription revenue expressed as a monthly value. On the other hand, annual recurring revenue is the sum of all subscription revenue referred to as a yearly value.
The formula for MRR is as follows:
KPIs for product managers
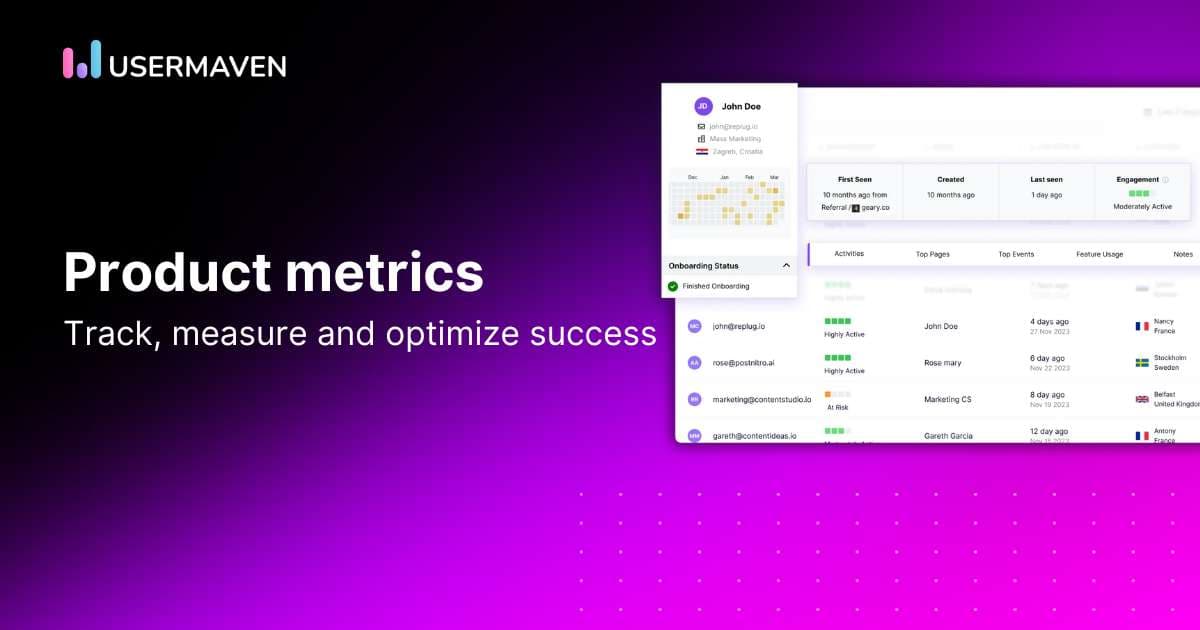
As a product manager, you must define your product’s goals, ask relevant questions, and set up indicators to track your progress. For product managers, KPIs help solve problems, manage risks, prioritize activities, and delegate tasks to team members. Focus on the relevant metrics to provide you with the most productive insights without consuming your resources.
Measure the key metrics on a product analytics tool to give you a summary of product performance and share them with the top management and stakeholders.
How to make product improvements using product metrics?
Tracking the product’s performance and adding value are possible with the right metrics and tools. In a customer journey, there are numerous product metrics to measure. They are broadly divided into the following five categories.
- Acquisition – These metrics measure new sign-ups, product usage, and onboarding KPIs. They help you see which marketing channels effectively lead to product adoption.
- Activation – It is a point when the customers first derive value from the product or a feature. You guide your customers through every step by introducing them to your product’s benefits. This is your customer’s success moment that motivates them to become loyal customers. Activation rate and time to activation are some of the activation stage metrics.
- Engagement – Metric in this category tell about the extent to which the customer stick with the product to gain value. They measure how often and how long customers engage with your product, like monthly active users.
- Retention– Retention metrics like churn rate measure how many of your customers continue to use your product over a while.
- Revenue – This metrics category is about how delivering value to customers makes the business money. Net revenue retention, recurring revenue, and average revenue per user are some income-related product metric examples.
Depending on the nature of your product, implement the metrics that best describe your customer journey. While setting up the customer journey and metrics, keep the ideal buyer’s persona in mind. The customer intent is the holy grail of what product managers want to understand and influence. Customer intent is the thoughts directing a customer’s actions and decisions toward a specific purchasing event.
You might also find this interesting: Strengthen your Customer Journey
Use product analytics platform to track product metrics!
Product metrics are an integral tool for the product manager to predict product performance and revenue generation accurately. Usermaven is the trusted choice of product managers to complement their product strategy. It is an easy-to-use tool that offers actionable insights for product-led SaaS Growth. You can measure and keep track of the product metrics for every stage of the customer journey.
See Usermaven in action
Book a free demo and discover how powerful analytics can grow your business.
*No credit card required
Try for free
Grow your business faster with:
- AI-powered analytics & attribution
- No-code event tracking
- Privacy-friendly setup