9 Key marketing insights for product managers
Oct 19, 2023
6 mins read
Written by Usermaven
Do you know that 95% of new consumer product launches fail? So, what can you do to ensure your product is not one of them?
While the success and growth of a product involve many factors, one of them is having a well-rounded product manager. Product managers are there for a product as it goes through the stages of inception, development, launch, and beyond.
They not only ensure fruitful development but also take the developed product to the market so it generates revenue. Both product management and marketing are essential pieces in the product success puzzle.
In this article, we will explore what product marketing means and how product managers can leverage it to ensure growth through the different product life cycle stages.
Who is a product manager?
A product manager (PM) is a professional responsible for monitoring the development, strategy, and success of a product or product line within a company. Their primary goal is to ensure that the product meets the target customers’ needs and achieves the company’s strategic objectives. The role of a product manager is multifaceted and involves a combination of business, technical, and design skills.
The product manager’s highly collaborative role requires strong communication and leadership skills. They are the single point of contact for different teams. A product manager is a vital part of product development, from planning to launch and further.
What is product marketing?
Product marketing is the sub-domain of marketing that focuses on promoting and bringing a product or service to the market. It bridges the gap between product development and sales, ensuring that a product meets customer needs and achieves revenue and growth goals. Product marketing involves creating and executing strategies that drive product awareness, demand, adoption, and success in the market.
Product marketing is intimately connected to the product life cycle. Product marketers are central in shaping strategies and devising product messaging and positioning. They choose marketing tactics to effectively market a product through its life cycle, from introduction to decline. Their objective is to maximize product success and impact in the market.
Power up your SaaS
with perfect product analytics
*No credit card required
Insights a product manager should have a grip on
Product management is a versatile role that requires a keen understanding of various critical aspects. Therefore, understanding the product marketing landscape is essential for product managers to ensure they develop a product their audiences love. Let’s explore the nine key areas a product manager should have a firm grip on to drive product success.
1. Brand personality Is more vital than ever
Brand personality is essential for product managers to consider, as people today want to feel connected to the brands they use.
A brand’s personality is a set of traits and characteristics that define how customers perceive the brand. When product managers align their products with the brand personality, they help create a strong emotional bond with customers. This bond goes beyond buying things and makes people feel like they belong to something meaningful.
Brand personality can be a great differentiator in a competitive market. When product managers design products that embody the brand’s personality, it helps the brand stand out and create a unique identity in customers’ minds. So, for product managers, knowing the brand’s personality isn’t just a nice-to-have; it’s the key to building a loyal customer base in a competitive market.
2. Strategies based on customer persona
A buyer persona represents the archetypal profiles of your ideal customers. Understanding these personas helps product managers maintain a customer-centric focus when developing and prioritizing product features. PMs can make informed decisions that align the product with actual customer demands by considering specific buyer personas’ needs, preferences, and pain points.
Product managers can prioritize development efforts critical to the product’s success based on the personas. Not all features will be equally relevant to all buyer personas. And different personas may respond to different value propositions and messaging approaches. By understanding these differences, product managers can create more persuasive marketing content and product positioning.
3. Right implementation of the marketing strategy
Product managers can play a critical role in implementing the right marketing strategy. By closely collaborating with the marketing and sales teams, they provide valuable insights and a deep understanding of the product’s capabilities and customer needs.
PMs that help implement the right marketing strategy ensure that customers understand the product’s benefits and how it addresses their pain points. This clarity is essential for successful product adoption and market penetration. They also provide continuous feedback on customer preferences and market trends. It allows the marketing team to make necessary adjustments and improvements to the strategy. Furthermore, product managers work closely with cross-functional teams to ensure that the marketing strategy is in
line with the product’s development roadmap and long-term goals. This helps maximize the product’s market potential and enhances its competitive advantage.
4. Solid document creation
Product managers should never underestimate the power of solid documentation. They are critical for communicating important information about the product to customers, prospects, and internal teams. Clear and well-structured documents ensure that everyone understands the product’s features, benefits, and how to use it effectively.
Customers rely on user guides and documentation to learn how to use the product, troubleshoot issues, and get the most value from it.Internally, these documents aid in training sales, support, and customer success teams, making it easy to convert PDF to SCORM for scalable training, ensuring they have the knowledge needed to assist customers.. They can be used in addition to mentor matching programs, which are also beneficial in providing on-the-job guidance and support for new employees.
Below is a list of documents a product marketer creates and maintains.
| Product Datasheets: Concise documents detailing essential information about a product. |
| Whitepapers: Comprehensive reports or guides providing in-depth analysis or solutions to specific topics. |
| Case Studies: Detailed accounts of real-world scenarios demonstrating how a product or service solved a problem. |
| Presentations: Visual materials used to convey information or ideas to an audience or internal teams. |
| Demo Videos: Videos showcasing the features and functionality of a product. |
| Infographics: Visual representations of information or data for quick understanding. |
| Product Videos: Videos highlighting a product’s features, benefits, and use cases. |
| User Guides: Manuals or documents providing instructions on how to use a product. |
| Testimonials: Statements or endorsements from customers sharing their positive experiences with a product or service. |
5. Developing a responsive product pricing strategy
Product managers can play a vital role in developing a responsive pricing strategy by carefully analyzing the market landscape. By conducting comprehensive market research and closely examining competitor pricing strategies, they can gain valuable insights into pricing trends and customer behaviors. By evaluating the benefits and advantages offered, they can effectively communicate the value of the product to customers, thereby justifying the price point and distinguishing the product from its competitors.
Incorporating customer feedback into the pricing strategy is another key area where product managers excel. Actively seeking and integrating customer perspectives on pricing enables project managers to understand how customers perceive the value of the price paid. This integration allows for necessary adjustments to the pricing strategy, ensuring that it remains attractive and responsive to customer expectations.
Collaborating closely with sales and marketing teams, product managers ensure that the pricing strategy is in line with the broader business objectives. This guarantees that the pricing approach supports the overarching sales and marketing goals, thus creating a cohesive and effective pricing strategy.
Related: Decode The Science Behind SaaS Pricing Models
6. Analyzing user journeys by setting a feedback loop
Analyzing user journeys is another core area a product manager should have a strong grip on. Here’s why!
Analyzing user journeys provides insights into how customers interact with the product at each stage of their experience. This deeper understanding helps product managers align product development and marketing strategies with customer needs and preferences.
By tracking user journeys, product managers can identify pain points, bottlenecks, and areas where users may struggle. These insights can inform UX/UI improvements and feature enhancements to create a more user-friendly and satisfying experience.
A feedback loop enables product managers to gather continuous feedback from users. This feedback can drive iterative product improvements, ensuring that the product remains relevant and valuable in users’ eyes.
7. Setting up multiple audience touchpoints
A product manager should never compromise on setting up multiple audience touchpoints. Different customers have varying preferences for how they interact with brands and products. Some prefer email, while others prefer social media, chat, or in-person interactions. Product managers and marketers can cater to these diverse preferences by having multiple touchpoints.
Each touchpoint represents an additional opportunity to reach potential customers. By diversifying touchpoints, businesses can extend their reach to a broader audience and capture potential customers who may not have been reachable through a single channel.
Multiple touchpoints allow for more frequent and varied interactions with customers. This increased engagement can lead to higher brand awareness, customer loyalty, and stronger relationships. The flexibility to choose the most convenient and comfortable way to engage with the brand or product enhances the overall customer experience and increases customer satisfaction.
8. Understanding past customers can be your greatest asset
Past and current customers hold immense value for a business, and product managers should be aware of this fact. These customers are more likely to make repeat purchases. And building loyalty with existing customers can lead to a steady and predictable revenue stream.
Moreover, acquiring new customers can be costly in terms of marketing efforts. Therefore, product managers help focus on marketing to th
eir existing customer base, who are already familiar with the product and brand. Satisfied customers can act as advocates, an organic form of marketing practice. It can lead to new customer acquisitions through referrals.
Additionally, past customers are ideal candidates for cross-selling related products or upselling to higher-tier offerings. It is crucial information for product managers when expanding product lines or creating product bundles. Furthermore, based on their product experiences, their feedback is invaluable for product managers. They use it to make data-driven decisions for product improvements and address any pain points or issues. By understanding past customers’ preferences and purchase history, product managers can tailor their product recommendations effectively, leading to increased customer satisfaction and product success.
9. Measuring success with data analytics
Product managers can leverage data analytics to measure the success of their product marketing strategies. Data analytics provides empirical evidence of what works and what doesn’t. By analyzing data, product marketers and managers can make informed decisions, allocate resources effectively, and optimize strategies based on measurable outcomes.
Data analytics offers an objective way to evaluate the performance of marketing campaigns, product launches, and other initiatives. It removes subjective biases and clearly shows whether goals and KPIs are being met. Measuring success through data analytics allows product managers to calculate the return on investment (ROI) for various marketing activities. It helps determine which activities provide the best value and which may need adjustment or reallocation of resources.
Data analytics provides insights into customer behavior, preferences, and demographics. These insights can inform a product marketing agency‘s strategies, allowing for more targeted and personalized approaches that resonate with the target audience. It also enables ongoing optimization. Product managers can identify areas for improvement, conduct A/B testing, and refine strategies to increase efficiency and effectiveness over time.
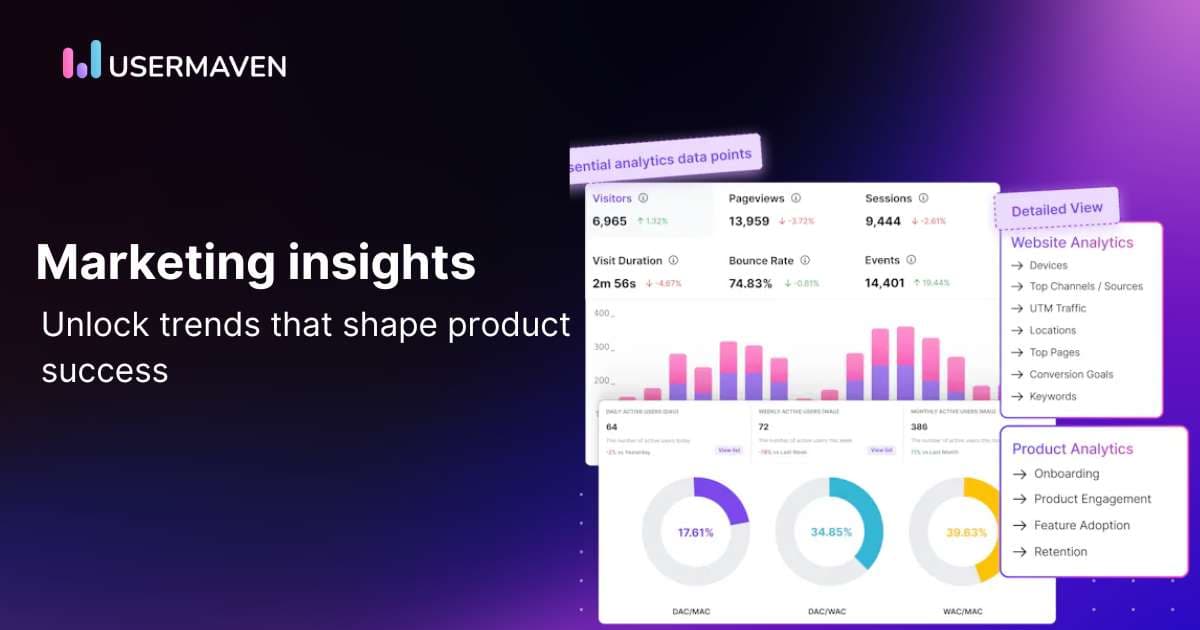
Project managers can use website and product analytics tools for this purpose. Tools like Usermaven empower them by offering actionable insights for product-led business growth. Product teams and marketers rely on it to gather user insights regardless of the customer journey stage Whether it is the acquisition, customer onboarding, product engagement, feature adoption, or retention, Usermaven is one solution product managers trust for their dynamic product success needs. Here’s a brief feature overview and how it supercharges product marketing:
- Acquisition: Funnel analysis allows PMs to visualize drop-off and conversion rates, and marketing attribution features tell which marketing channels work.
- Customer onboarding: PMs can find out the blockers users face while onboarding, and they can smoothen customer onboarding.
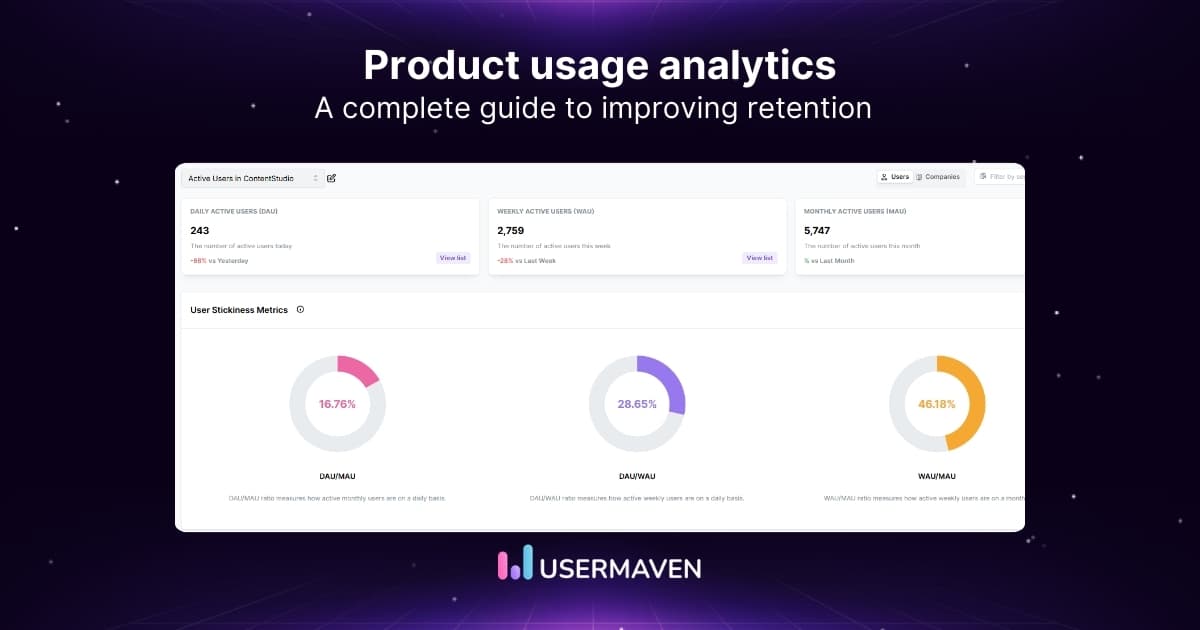
- Product engagement: Engagement metrics, stickiness ratio, power users, and more allow PMs to measure user engagement with a few clicks.
- Feature adoption: PMs can discover how customers use different product features and what areas need improvement.
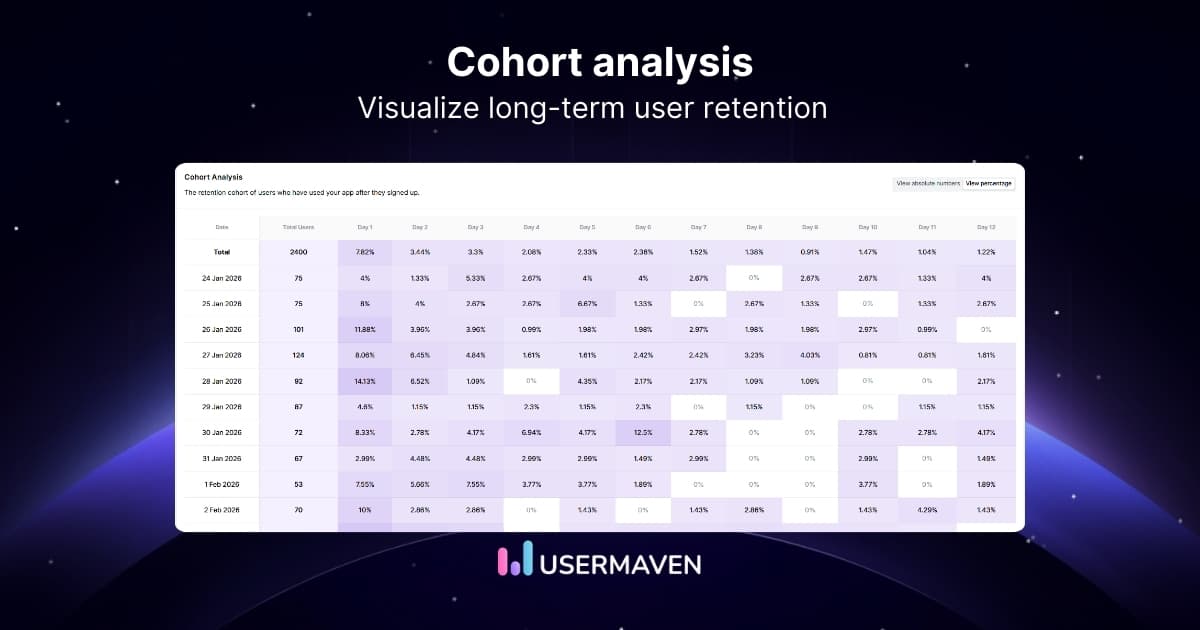
- Retention: Retention cohort analysis and tracking of users that are slipping away are powerful features PMs can use to reduce churn.
Conclusion
To sum up, it’s crucial for product managers to understand the ins and outs of product marketing to ensure the success of their products. With so many new products failing, it’s essential for them to know all about product marketing. They need to understand the brand’s personality, the different types of customers, how to do marketing well, the importance of good documents, setting the right prices, and how to keep customers happy.
Also, they should be good at looking at data to see how well things are going. One tool that can help with this is Usermaven. It can tell them lots of things about how customers use the product, what they like, and what they don’t like. By using tools like this, product managers can make sure their products do well in the market. So, if you want your product to succeed, don’t forget to check out Usermaven!
See Usermaven in action
Book a free demo and discover how powerful analytics can grow your business.
*No credit card required
FAQs
Who is a product marketing manager?
A product marketing manager is a professional responsible for a specific product’s marketing strategy and promotion. Their role is integral to product development and marketing. They ensure a product is effectively launched, promoted, and sold to the target audience.
How do product marketers and product managers work together?
Product marketers and managers collaborate on the product’s development and promotion. Product managers define features, and product marketers craft strategies based on the product’s value proposition and target audience.
What are the 4 main pillars of product marketing?
The four main pillars of product marketing are product, price, place (distribution), and promotion. These pillars collectively represent the key components essential for a successful marketing strategy.
What is the difference between PM and PMM?
Product Managers (PMs) oversee product development, making crucial decisions about features, while Product Marketing Managers (PMMs) focus on product promotion, creating strategies to boost awareness and demand. Together, they ensure the product aligns with customer needs and business goals.
Try for free
Grow your business faster with:
- AI-powered analytics & attribution
- No-code event tracking
- Privacy-friendly setup